Finding Information about Healthcare Quality
Healthcare Quality
- How is quality measured?
- How is it reported?
- How do you know if information is reliable?
- What web sources are available?
How Is Quality Measured?
Healthcare professionals, government agencies and consumer groups are continually looking for ways to improve the quality of healthcare – and to make quality information more consistent, reliable and helpful to consumers. To achieve these goals, quality experts rely on systematic ways to measure performance.
Currently, two major types of quality measurement are used:
- Consumer Ratings give you other people’s thoughts and opinions about their healthcare experiences. These ratings are based on individuals’ personal points of view. As an example, most major hospitals conduct satisfaction surveys to gauge patients’ perceptions of the care and service they received.
- Clinical Measures evaluate healthcare providers’ performance in preventing and treating medical conditions – including complying with established clinical practice guidelines based on the latest scientific evidence. For example, one measure for assessing care for a heart attack is whether or not the patient is given an aspirin immediately upon arrival at the hospital.
How Is Quality Reported?
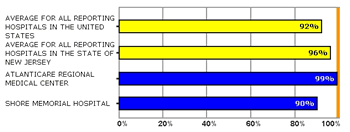 Sample chart from Hospital Compare on the percent of heart attack patients given aspirin at arrival
Sample chart from Hospital Compare on the percent of heart attack patients given aspirin at arrival
Quality reports – often referred to as Report Cards – are published by a number of organizations and can be helpful to you in selecting a treatment option or a healthcare provider. Use these reports along with the recommendations you receive from your physician, your health plan and other professional sources.
Report Cards are available online:
- Hospital Compare
Sponsored by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, this report shows recommended care for adults being treated for heart attack, heart failure and pneumonia and for those undergoing surgery. The site also shows how often hospitals provide that recommended care to get the best results for most patients.
How Do You Know If Information Is Reliable?
Ask yourself these questions:
- Who is the source of the information? Is it a person or organization that is well recognized and respected in the field of healthcare? Is the author credited and is he/she an expert in that area? For Report Cards or other ratings, is the group publishing the information unbiased? Reliable sources include:
- Hospitals and other healthcare organizations;
- Associations, such as the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations;
- Government agencies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- How current is the information? Most reports and information are dated and indicate the time period they cover. You want to use the most up-to-date sources.
- If you are gathering information on the Internet, does the site you are using appear well maintained? Look for indications that the information has been updated recently. Also, links to other web sites should be working – not broken.
What Web Sources Are Available?
Online information regarding healthcare quality continues to become increasingly available. We suggest these sites as a starting point.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality:
Part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, this agency works to improve healthcare quality, prevent medical errors and assess the results of care provided. - American Hospital Association:
Learn your rights and responsibilities as a hospital patient by reading a downloadable brochure called "The Patient Care Partnership." - American Nurses Association:
Through its Magnet Recognition Program, the ANA recognizes more than 180 healthcare organizations for excellence in nursing service. Nursing Magnet designation is considered the gold standard for quality in the nursing profession. ANA’s site includes a facility listing of those hospitals – including AtlantiCare Regional Medical Center – that have attained Magnet status. - Hospital Compare:
Sponsored by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, this report shows recommended care for adults being treated for heart attack, heart failure, pneumonia and for those undergoing surgery. The site also shows how often hospitals provide that recommended care to get the best results for most patients. - The New Jersey Hospital Performance Report:
Sponsored by the New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services, this site was created to provide hospital quality information to patients, their families, and health care professionals. The information is designed to help you choose a hospital and make other decisions about your health care. The report shows how each hospital treats eligible patients with a heart attack, pneumonia, or congestive heart failure. - Institute for Healthcare Improvement:
IHI is a non-profit organization whose purpose is to improve the quality and value of healthcare. Its focus is healthcare safety, effectiveness, patient-centeredness, timeliness, efficiency and equity. Among its programs is the “100,000 Lives Campaign,” which aims to enhance patient care and prevent avoidable deaths.